Blog Tag: Android
How to Choose a Mobile App Development Company? – A Comprehensive Guide

Choosing an outsourcing partner for your next mobile app is everything but easy. First, there is endless number of mobile application development companies out there. Try to Google, ‘mobile app development company’ and you’ll understand what I mean here. Apparently, Google is the best place to look for an app development company.
With so many companies showing up in Google search results, it’s easy to get lost. However, don’t lose your hope already. There are some neat tricks and after a little scrutinizing to the parameters, which I am going to present by means of this blog, you’re going to run out of quality mobile app firms to choose from.
Preps
One of the major problems with firms looking to outsource mobile app development is this that they start searching and approaching firms without gaining any intelligence into the market or perfecting their app idea. This anomaly makes them an easy target of fraudulent app developers that disappear somewhere upon the receipt of payment.
Gathering intelligence
You’re not the only firm looking for an app development company. There are many on the same trail. The only difference is this that many of them are not doing this for the first time. With mobile development getting larger every day, every firm wants to make money out of it. No doubt, there are so many companies out there, confusing the hell out of you.

When you approach a company over a cold online search, it expects you would have done some sort of research. When it realizes you did not, they are going to either over-quote you or won’t take you seriously.
I would recommend going through a few YouTube videos and a number of blogs to get a basic understanding of mobile app development before running the hunt.. While the pricing varies greatly from firm to firm and geographies, you should get a fair estimation how many hours it will take to bring the app to the market.
In addition, you can meet some local mobile development companies in your area to gather intelligence.
Shortlisting the firms
As I said, the internet isn’t short of companies that stuff “mobile app development company” in their webpages. However, not every company that stuffs the keyword to manipulate Google search algorithm in its favor develops mobile apps. So are mere vectors to actual companies. Beware! these agents disappear as soon as they get their commission.
Nevertheless, it’s not hard to tell an agent from an actual development company that specializes in mobile app development.
Tip: Remember, a website shows only the best of a company. If you want to learn the truth, look elsewhere.
When you look for an app development company in Texas, you will encounter three types of websites: development companies in Texas or operating in Texas, a website that lists such companies, for example, Clutch and GoodFirms, and education websites teaching you how to develop an app.
Is outsourcing abroad safe?
While outsourcing development to a firm in the states is a much safer option, a mobile development company easily charges anywhere $100-$150 per hour in the US, which isn’t affordable unless you’re fine spending upwards of $50000 in mobile development alone. On other extreme are mobile developers in Bangladesh and the Philippines that are ready to work for less than $10 per hour. If you are looking for a balance between cost and quality, you can pick East Europe and India.

I personally prefer India as developers there are much more fluent in English than developers in Europe. Also, it’s easier to find a development company in India that is ready to work for less than $40/hour.
Check Portfolio then Crosscheck
Most of the development companies demonstrate their portfolio on their websites. If a certain website you shortlisted do not, it’s ok to ask for it. Most websites have a contact us page to contact the administrator.
Once you have hands-on the portfolio, try to contact the companies whose portfolio has been shared with you. It’s easy to find their contact info as long as their websites have a contact us page. Don’t be shocked if you find a few companies that fail to recognize the developers. In the mobile development market, ‘fake till you make it’ is a common mantra.
I’ll suggest you drop such developers already and go with only those developers whose portfolio you could validate. Credible mobile development companies won’t hesitate from sharing the info about the client they worked with unless an NDA is involved.
Raise an inquiry
It’s time to contact the shortlisted development companies. At this stage, you do not have to share any info about your idea or the app. Just let them know that you’re interested to work with them on an app. Most of them, will contact you back within a couple of days to gather ideas and details for the app you are looking to develop.
Commonly, development firms expect the interested parties to share their contact information on their website from the contact us page. A few firms also offer you free estimation or consultation on request.
A word of caution!
Do not share any details of the app or your ingenious app idea unless the development company has signed a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) with you. Once they have signed the document, they are under legal obligation not to disclose any info about the app to anyone. NDA will give you creative and technical freedom to share your thoughts with all the shortlisted companies.
Passing the info is important for development companies to understand the scope of your work and translate into the number of man-hours required and, ultimately, cost.
Negotiate the cost
Once the shortlist is ready, try to negotiate the cost for the number of features available. Most of the development firms are more flexible with pricing if you commit them long term development plan or give a handful of references. You will be negotiating with more than one firm at a time so keep a tab of the price you last negotiated with a firm.

You can make the final decision once you have all of their prices. It’s apparent to go with the lowest price but there are more factors to consider. A major one is a features-to-cost ratio—the greater the ratio the better the deal you’re getting.
Remote Team
You will be working with a virtual team sitting somewhere on the globe. Most firms let you interview and select the members of the cloud team. Remember, you’re going to pay them hourly. So this may occur to you: you don’t need the most efficient person who can deliver the maximum in minimum time. A senior developer will help you make most of the hours you’re going to pay for. However, they are costlier.

A balanced team is consists of a couple of senior developers and 5-10 junior developers working under the command of a supervisor. Selecting candidates for your team is a one-time process. Most companies to cut down chaos allot you a single point of contact, mostly a team leader or a project manager, depending upon the size of the project.
In case you find the developers not up for the job, it is better to look elsewhere probably for a higher cost.
Go Agile
This goes without saying but most new companies looking to develop a mobile app rush through their apps development cycle and try to stuff more features that it can take. This rush leads to the development of an app with half-baked features and too high a cost.
The biggest benefit of going agile is that new features are added gradually. So you have more time to test the features of an MVP. In addition, the developer will bill you for only the features he added, which will help you keep costs in check.
Hire TOPS Infosolutions
If you are looking for a mobile app development company that works with a global clientele and has presence in various countries, there is no better app development company but TOPS Infosolutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do you practice the Agile App Development Process?
Indeed we do. The most significant advantage of going agile is that you can add new features progressively. So, this gives more time to test the features of an MVP. Additionally, we will bill you only for the added features, which will significantly keep the costs in check.
How secure is my app during the development process and post that?
We follow strict ethics when it comes to confidentiality. We encourage our clients to sign a Non-disclosure agreement (NDA) which entitles us to be under legal obligation not to disclose any app-related information to anyone. So, you need not worry about it.
Will You Maintain My App Post-Launch?
We support maintaining your app post-release. Our developers at Tops are available around the clock to offer maintenance assistance.
What will be the cost involved to develop an app?
The cost varies according to the various features and aspects that your application demands. The timeline and workforce allocated also play a significant role in determining the cost. To know exactly how much it would cost for development, drop us your requirement, and our experts will get back within 24 hours with a free quote.
How to Setup a Mobile-first On-demand Delivery Business?

Who doesn’t love the idea of getting their favorite pizza delivered home? If you’re a restaurateur delivering food to the location, it’s a win-win situation for you. You can cater to more diners than the sitting area in your restaurant allows, which means more business without additional investment into real estate.
Let me give you an example, suppose, you run a little diner in your backyard that can accommodate 20-30 people at a time. Your average income per diner is $2 and every day you welcome 200 such diners, making an estimated $12000 every month.
Now suppose you open your doors to home delivery and hire a delivery boy. The delivery boy delivers 30 food packets every day and you have set the minimum order amount to $10. Now, you’re making an additional $10000. Even if you deduct the expense on the delivery boy. This is still an incredible deal.
Had you invested in additional real estate for the restaurant, that would have cost you anywhere between $40000-$100000.
However, managing a food delivery business or any type of on-demand delivery business is a lot more complicated than the example above is. Let’s take a look at what it takes to run an on-demand delivery business.
On-demand Delivery Business from Boom to Bane

We have grown many times since the first pizza home delivery service started. What happened in the meanwhile is this that soon restaurateurs got overzealous with the whole idea of increasing business income without substantial investments. Every restaurant started some form of phone ordering business. It was so much booming that online orders soon took over diners sitting at the restaurant. Soon restaurants were getting far more order requests than their tele-callers could handle, kitchen could cater to or delivery boys could deliver. The growing competition means thinning profit margins. The system crumbled under its own weight and proved inefficient at the end of the day.
Many restaurants capped no. of phone order they will take, thus, putting a full stop to the boom.
The Reincarnation around Mobile and Cloud
In July 2010, an app-only taxi-hailing app was doing rounds in tech circle of San Francisco, at the heart of the Silicon Valley. Many called the app at the forefront of latest mobile and cloud technology revolutionary. The idea was simple rather than going to the taxi the taxi will come to you with a single tap on your iPhone.
The ingenious idea soon infested other industries including the vulnerable food delivery and later professional services like plumber and baby sitter, even a doctor.
By the turn of 2015, everybody from your local grocer to your favorite restaurant to the baby sitter who lives next door were part of one of the various on-demand marketplaces mushrooming on the app stores and catering to local businesses and professionals in your area.
The decreasing cost of Android phone, a rising middle class, and affordable cloud computing services were the principal contributors to the reincarnation of on-demand delivery business.
The On-Demand Boom
The success of Uber gave confidence to many industry pundits in renewing mass’s interest in on-demand delivery business. After all, mobile applications are much more capable than dumb phone calls to telecallers. This gave way to on-demand boom. Every startup or industry player wanted to capitalize on the new playground given birth by Uber in chassis of a mobile app
Soon, there was an Uber clone for every sort of thing or person whether a person wants a plumber to fix a dripping faucet in his living room, monthly grocery delivered at his place or taxi or Uber to head to the next meeting.
As I said there are all sorts of on-demand marketplace for everything or person you can think of. So is the number of players competing in the space and apps for each of them. This is where the term came, “There must be an app for it.”
The Power of Local Provisioning
On-demand delivery apps are relevant because local businesses and professionals back them. Those apps are only the marketplaces that connect with the local providers or businesses. While the latter can work with the former, that is not the case the other way around.
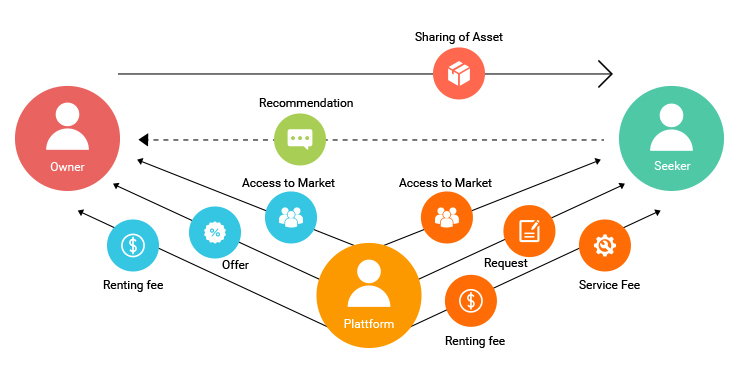
If you’re looking to enter the opportune market yourself, you’ll have an edge if you have influence in the local market. You need people to deliver what your users demand. If you’re a grocer, then you need delivery boys to deliver grocery. If you are cab company, then you need drivers to drive your cars around and if a home services provider, then you need a number of handymen ready to deliver services to your users.
In a nutshell, you need to convince a lot of people to join your app-based marketplace before you seek an app developer to build the app ecosystem around your marketplace.
What is Driving the Interest?
At the center of on-demand economy, is a powerful ecosystem of mobile apps. No doubt, mobile app developers have been constantly busy since Uber came. There are all sort of startups keeping them busy and they have every reason to.
The investment in on-demand startups has grown more than 1400% from $74 Billion in 2014 to $10,293 Billion in last quarter of 2017. Moreover, an on-demand startup has better chances of capturing seed funding, a study by CBInsight indicates.
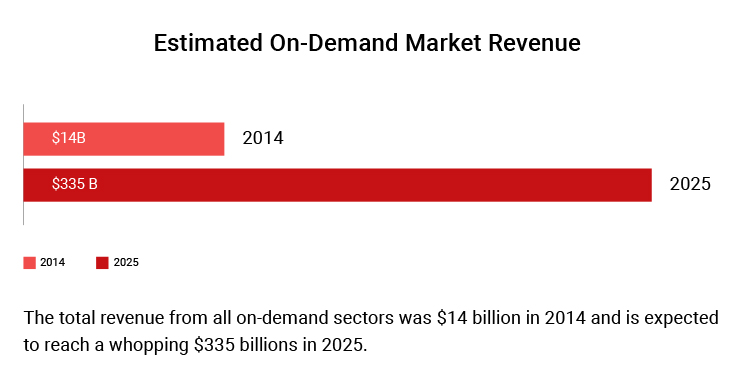
And it’s not just the investors interest. The revenue from on-demand economy will multiply 23 times from $14B in 2014 to $335B in 2025, predicts PwC
Evidently, users’ spending in the on-demand mobile app economy is rising at unprecedented pace. The total spending from year 2016 to 2018 grew 58%, National Technology Readiness Survey. Some of the sectors that received the largest piece of pie were online marketplace, transportation, and housing. Food delivery, surprisingly, came 4th in terms of investment but grew maximum in the period, Rockbridge report suggests.
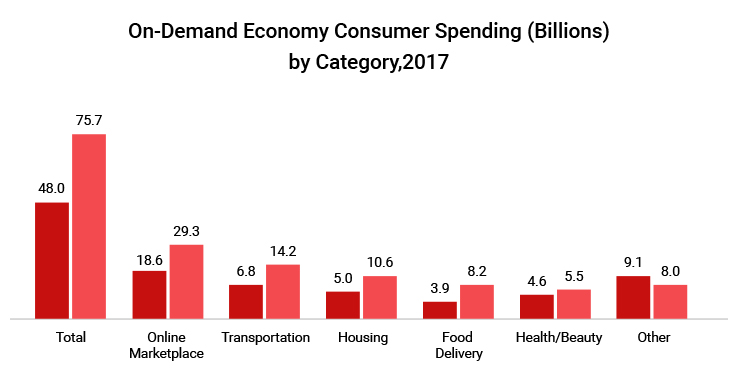
Building the App Ecosystem
While those are great numbers, on-demand services won’t have existed in the first place had it not for mobile technologies and applications. If you have used Uber in the past, you know what I mean here. The level of convenience provided by apps like location awareness, turn-by-turn navigation, real-time locations sharing, in app chat and support and flexible payment options were unheard of before.
The Uber you use to book taxis is only a part of the app ecosystem. A larger part of the ecosystem is shared various players in the on-demand business and each role has a dedicated app.
In on-demand delivery business, there are generally two sets of people involved in addition to the admin, manager, or owner. Of course, at the center are the end users, who originate the demand. Then there are delivery boys who fulfil those demands.
Therefore, we need three apps: users, delivery boys, and merchants. Let’s take a look what their app look like.
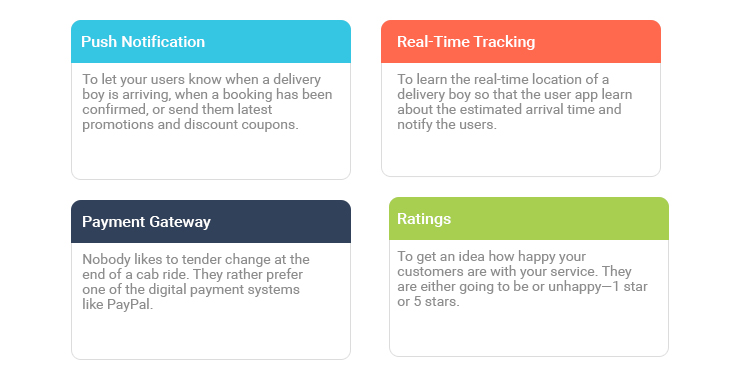
Users’ App
The user app originates the demand–what he or she wants. The app is simple, the users requests what he wants, when and makes payment—all in the app. Upon request fulfilment, he waits for the desired person to arrive and deliver him the thing or service.
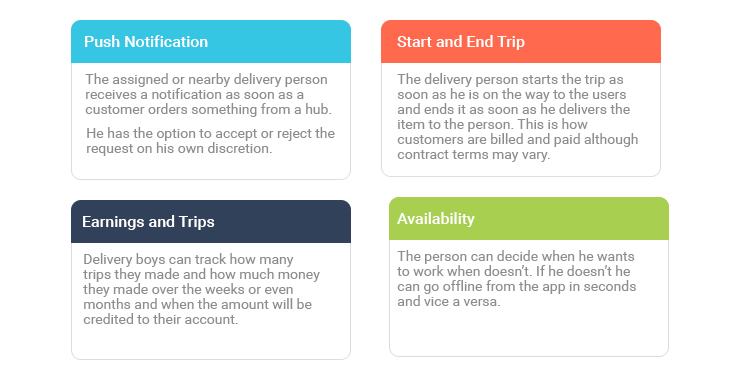
Delivery Persons’ App
In on-demand delivery business model, the delivery boys either pick up an item from a user or drop off an item from a user to a hub. So when I want a parcel collected from courier company and delivered at my doorsteps I use their app. Alternatively, when I want a food parcel from my favorite restaurant to reach me. I ask a delivery boy to deliver it to me, who picks the parcel from the restaurant, which acts as hub here.
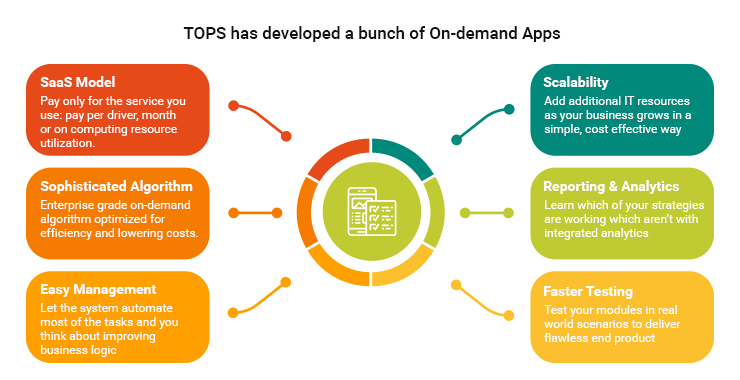
TOPS has Developed a Bunch of On-demand Apps
If you think developing on delivery apps is too much on your side, you can ask us to. Our team of mobile app developers has an experience of developing tens of on-demand apps. Being a top ranked, an award winning mobile app development company, we have a global clientele and worked with more than 300 different clients since inception.
There are many advantages of developing on-demand mobile apps with TOPS Infosolutions:
Final Remarks
TOPS has the reputation of delivering end-to-end IT solutions to startups into on-demand businesses. Companies around the globe prefer us for faster development time, advancing on deadlines, transparency, cost checking, above all, top of the line support.
React Native App Development Part 1: A Beginners Guide to React Native Architecture

Let’s take a look at one screen from an app that is purely React Native and ask ourselves what is the UI that we see here.
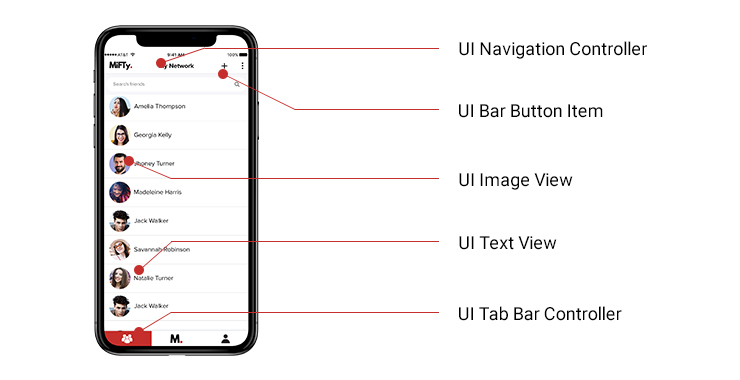
Is this an HTML? Is this a webview like other implementations like PhoneGap or Cordova?
The answer is, without a doubt, No. The views in React Native are purely native views so from our app the navigation controller that you see here the top bar is UINavigationController. Now, if you are an iOS developer you would these are the same UI views that you use in your native apps.
 If I had shown you the same screen on Android, you would see that the implementation is completely different. It renders to the native views. If the UI is completely native with React Native, where is the JavaScript?
If I had shown you the same screen on Android, you would see that the implementation is completely different. It renders to the native views. If the UI is completely native with React Native, where is the JavaScript?
Where is the JavaScript?
JavaScript is what running under the hood. Where you as a developer specify the business logic and which components you want and then the framework renders it for you. To understand this better, let’s dive into React Native a little deeper and see the architecture from the inside.
Understanding React Native Architecture
Consider there are two realms running side by side in your app. You have the JavaScript realm and you have the native realm.
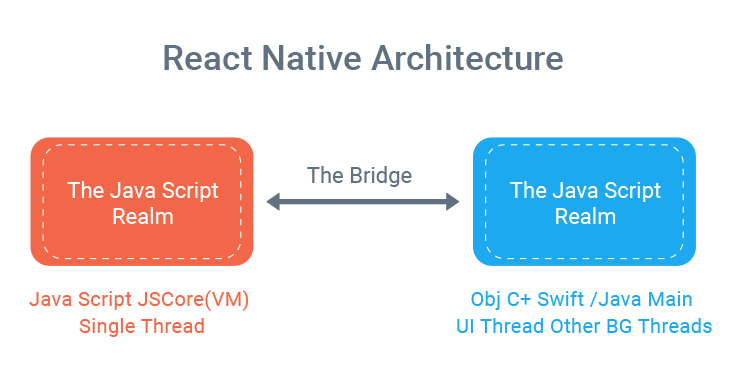
JavaScript Realm
The JavaScript realm is where you program in JavaScript, naturally. The code there is running on a JavaScript engine. Specifically in React Native it uses jscore, that is the open source JavaScript engine for WebKit. You are probably familiar with other engines like V8. They do the same things and this engine is running inside your app on one of the threads. Your app is a process that has several threads in it. JavaScript is just one of them.
Native Realm
In the native Realm, you still develop an objective C and Swift if you are on iOS or with Java if you are on Android. You use the native platform specific languages that you use before and you have the main UI thread as usual. In all platforms, you can usually change UI only from the main UI thread and you can create as many background threads as you want.
The Bridge
These two realms are different and connecting these two realms is the bridge. The React Native is a very important construct in this entire setup. Did you ever try to debug a React Native application using Chrome for example, so when you debug a React Native application using Chrome, then you have the two realms actually running on different computers. You can run the JavaScript role entirely inside Chrome itself.
You can debug it inside Chrome debugger and you have the native realm still running on your phone. Then instead of going inside your app, you would go through a WebSocket. The bridge, which is just a communication protocol, can travel over WebSocket as well.
Will React Native mark the demise of Native App Development?

You can use your existing web development skills and can produce native iOS and Android app using those skills. It’s completely possible to utilize your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript skills to develop native Android and iOS apps.
I’m not talking about hybrid apps or just an app wrapper around a mobile website but actual native apps–pure, native apps that you design in iOS using Swift or in Android using Java or Kotlin. Thanks to React Native, native apps can now also be developed with common web technologies: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
If you still don’t believe me that these apps can be really be awesome. Take out your phone and have a look at one of these apps: Facebook, Messenger, Instagram, Skype, and Airbnb. They are developed in React Native.

What is React Native?
Facebook was facing a lot of problems about redesigning their apps and everything. The problem was handling many users and rolling out new features. Facebook needed something more robust, fasts that can handle a lot of traffic as well as can be designed really quickly. The brilliant team at Facebook started working on a JavaScript library, which came to known as React.
The best part is React employs faster virtual DOM. Although React is a library, lightweight component can be injected anywhere. You can use react with PHP, MySQL, Firebase, MongoDB or any database system of your choice.
You must be wondering isn’t React for designing web applications? Consider React Native as the successor of ReactJS for mobile app development. All the things that you learned in React like components props, States, Redux, Modal, etc. are part of React Native as well.
The things that you learned in React can be applied in React Native in the same workflow. Components, props and states are all used in react native and thus you got your native application.
The dual advantage of React Native
In React Native unlike native Java and Swift codes, you don’t ever compile your app. You just reload it just like do you a website in a web browser.
Moreover, you don’t have to maintain two separate codebases for your application. For example, let’s say you are a business and I am application development company whom you have outsourced a mobile app project.
Of course, you want an app for both Android and iOS in addition to the web. It requires two teams one for each mobile platform: one team for Android application and one team for iOS application. Those you aren’t aware implementing the same, exact features in iOS and Android app require a lot of communication exchange between those teams: app features, deadline, delivery, client expectation and requirements, etc.
Performance vs. Native Code
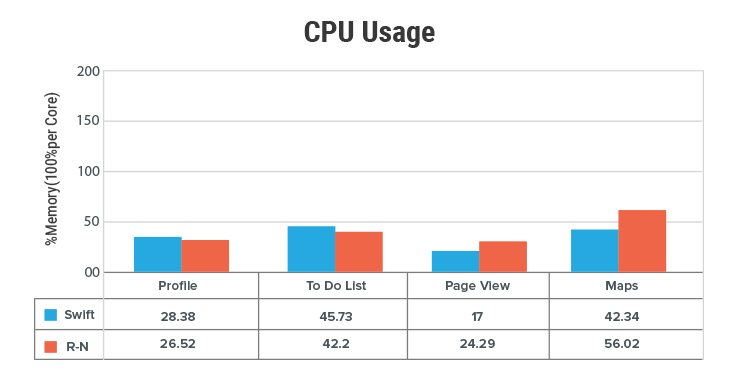
React Native apps perform, more or less, like an app written in Native iOS code. A Medium user ran a few tests to compare its performance with the native code and found performance at par with an equivalent app in Swift, sometimes even better. The Medium article measured performance in three areas: CPU, GPU and Memory utilization at the run time.
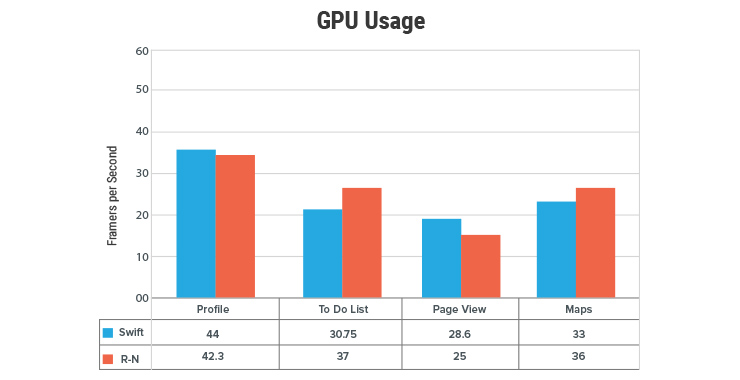
In CPU usage the performance was similar although maps performed better in Swift.
To calculate GPU performance, Native vs React Native, the author calculated frames per second (FPS) of the application under GPU load. Surprisingly, although by small margins, React Native outperformed Swift code by more 6.25 frames per second.
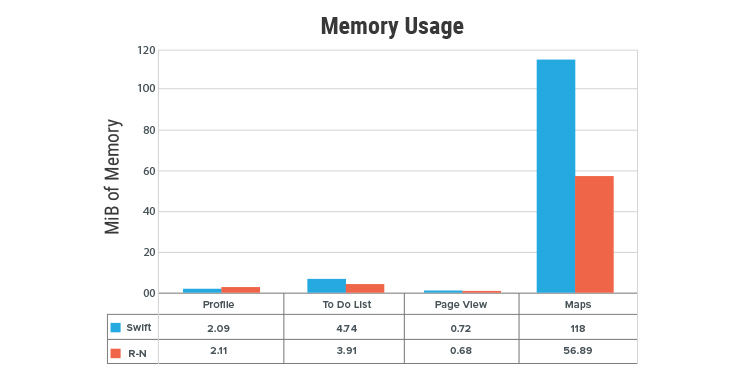
For memory tests, the author concentrated on maps as the memory footprints of other features was negligible to figure out a contrast. Evidently, at the peak performance, React Native used a whopping 61.11 MiB less memory than Swift. While performing the task and recording the measurements, a spike in Memory usage was observed at the exact moment, he pressed the “Maps” tab, which prompted the MapView to find my current location and highlight it with a blue, pulsating dot.
React Native is the smartest way to develop Mobile Apps
In the React Native, you just have to maintain a single codebase and that code will produce native Android app as well as iOS app. React Native is getting a lot of attention nowadays and people are loving how the things are shaping for React Native and the community is growing. You must be jumping on your couch. Finally, you can use cheaper web developers to design native Android and iOS app. You no more have to hire programmers or train them in Java, Kotlin, or Swift.
Is this the end of Native App development?
No, there existed always side-by-side technologies. Some businesses prefer React Native while others prefer native codes in Kotlin or Swift. It’s always good to have many mobile technologies around to choose from. Desktop application developers always had a lot of programming languages and technologies to choose from and most of them are still here, going strong.
For example, there are still apps that are being developed in Ruby on Rails, Django, PHP as well as node.js. Technologies evolve as per the demand.
The biggest takeaway of React Native is now there are more options than ever. Developers can go with Android development using Java or maybe Kotlin. Likewise, they can go for iOS development using Swift. With React Native, they have one more option to native development. Not to mention, now everyday web developers can also be part of native app development party.
The Tremendous Growth and the Future
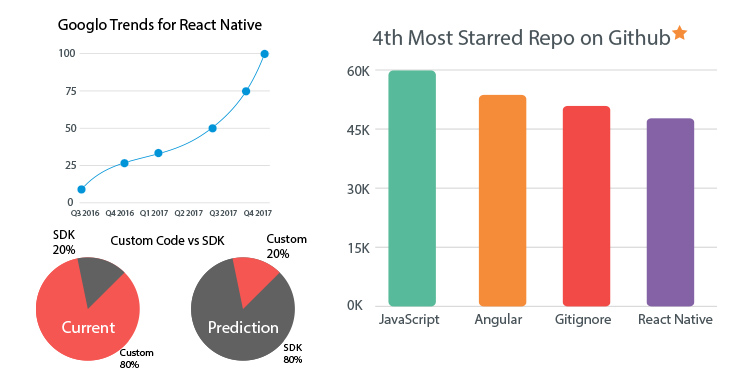
Nevertheless, React Native is growing at a tremendous pace and if the growth sustains, soon, we will find more React Native developers than those into Swift or Kotlin development. This development in mobile ecosystem will mark a huge shift from the traditional form of mobile development. The field will evolve to absorb React Native development or any similar emerging or upcoming technologies into mobile app development.
Google Trends is a popular tool to understand people’s interest in a search term. When used to forecast people interest in technology or a mobile development technique in this context, it can tell which of them are growing which are plummeting.
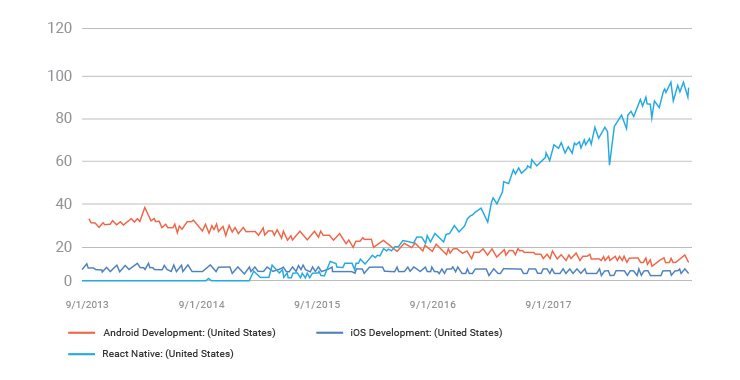
Source: Google Trends
Clearly, while React Native, as I said, has grown exponentially and iOS development has remained static, Android development has a seen a huge plunge. This made me think. Is the growth in React Native at the expense of Android development? It is too early to say but one thing is for sure: iOS development is here to stay while the future of Android because of React Native is in quite a disarray.
Android developers have a consistent complaint. They don’t earn as much as their iOS counterparts and the ROI is hard to come by. And the revenue gap is almost twice in a few demographics.
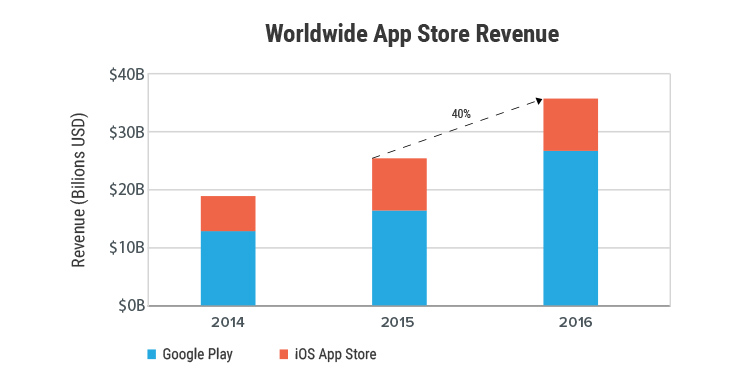
Source: App Annie
Perhaps, app platforms find React Native as the answers to their Android development vows.
Blurring lines between Android, iOS and Web development
The popularity of React Native and similar JavaScript frameworks are blurring the lines between web and mobile app developers. For the first in the history of mobile development, a developer can say I don’t want to learn Java or Objective C and still can build a mobile app.
For businesses looking to develop mobile apps, React Native brings a sea of opportunities. They can target both mobile platforms at the fraction of the cost. As businesses prefer iOS to Android for the reason I mentioned, React Native will give a new lease of life to Android development.
Android Pie: What’s in there for Developers

Android 9 or P will be called simply Android Pie. Google launched the 9th iteration of Android after more than an year of testing by early adopters. Android Pie is high on machine learning that is your phone will become smarter with time.
For developers, Android Pie gives you new ways to drive engagements and enhance your apps. So let’s look at what Android Pie brings for Android app developers. As I said, the highlight of this year’s Android release is machine learning. Machine learning makes the smartphone faster, long lasting, and easy to use.
-
Adaptive Battery
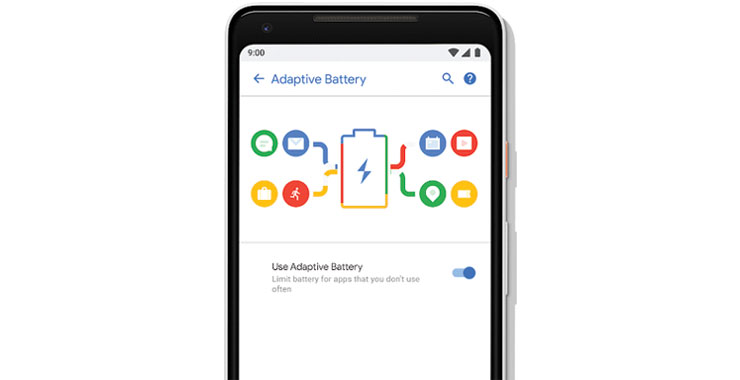
Source: Google Blogs
To save battery, Android Pie will restrict background activity of rarely used apps. If you’re a developer, make sure your app is optimized for Doze, App Standby, and Background Limits or adaptive battery will inhibit your app’s activities when the user will upgrade to Android Pie.
-
Slices
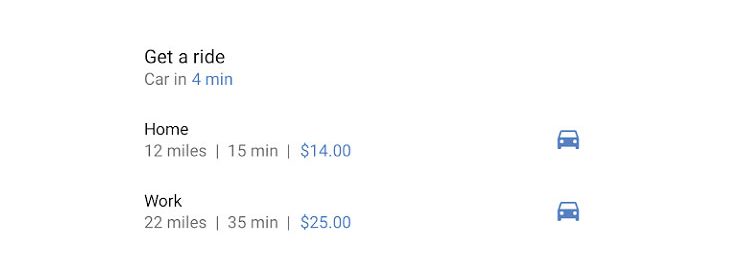
With Slices, you can enable UI templates that will display outside your app’s full screen experience. User can interact with these rich, dynamic elements belonging to your app from outside it like Google Search app.
-
Content Awareness
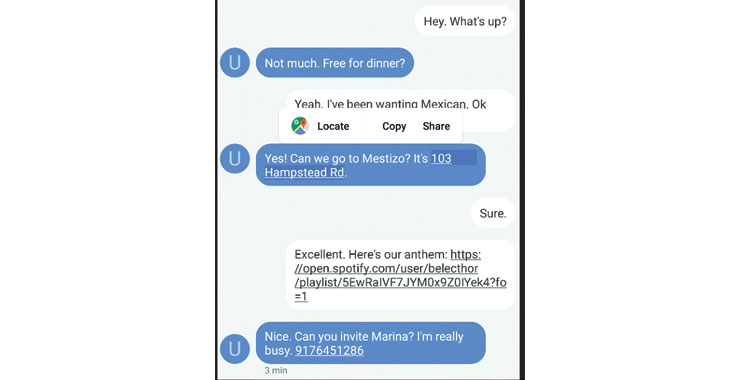
Developers can take advantage of the TextClassifiermodels which revolves around TextClassifier API. The model via Linkify API lets developers enable augmented options for quick follow-on user actions.
The machine learning model can identify object like Dates and Flight Numbers.
-
‘Notch’ is Supported
Android Pie officially supports notched displays now. The display cutout APIs contemplates the place, size and shape of the ‘notch’ and request full-screen layout around it. A developer Option simulates several cutout shapes to shape apps around them.
-
Smart Replies
The new MessagingStyle API displays conversations, adds photographs and stickers, and suggests smart replies. Developers can use ML Kit to enable smart replies on their app.
-
Text Magnifier
Android app developers can enable magnifier for all the view options. The Magnifier widget can zoom any view or surface, not mere text.
-
Biometric Methods
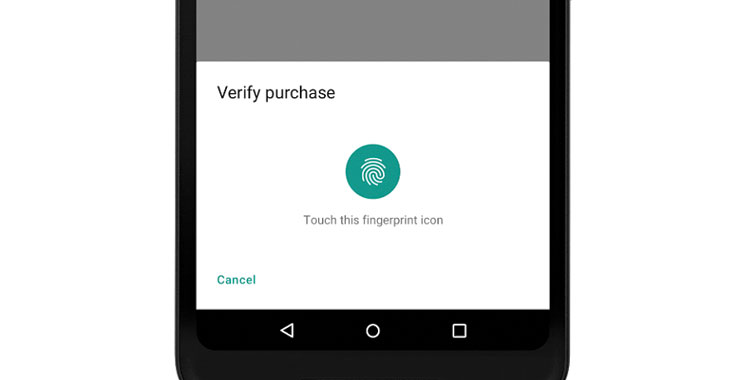
Developers no more have to build their own dialog for an app. Android Pie introduces BiometricPrompt API that has a stock system dialog. The API at this moment supports Fingerprint, Face and Iris authentication.
-
Android Protected Confirmation
Android 9 introduces Android Protected Confirmation to ensure that a prompt is indeed confirmed by the user and happened in a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE). The app can only verify prompt when TEE does.
This will keep the apps safe from false prompts that mimic system prompts.
-
StrongBox
StrongBox is the new KeyStore type that provides API support for devices that have secure, dedicated hardware to store keys. Keys should be protected by a StrongBox security chip in your KeyGenParameterSpec.
-
Default SSL
To raise user’s security, all the traffic to and fro from your app and application server will happen over a secure connection. Android Pie will block by default all exchanges between cleartext traffic.
-
More permissions
Android Pie will restrict idle apps to gain access to mic, camera and other sensors. Moreover, developers will now need READ_PHONE_STATE permission too to access build.serial. Android app developers can use Build.getSerial() method.
-
Multi-camera API

Android Pie natively supports more one streams of open camera in an app for the devices that support multi-camera API and have two or more camera setup. You enable features like loss less zoom, bokeh, and stereo vision.
-
HEIF and HDR VP9 image encoding
Android Pie support HDR VP9 Profile 2 on HDR capable devices. In addition, it adds HEIF image encoding. HEIF format compresses image without loss in quality. Developers can use ImageDecode for jpeg-to-heic conversion.
-
Dynamics Processing API
With the API, developers can filter out certain sound frequencies when a user plays audio from their app. If a person is speaking in loud environment, the API can filter out the noise.
-
ImageDecoder API
The API makes it easier to decode images to bitmaps or drawables. Apps can create bitmaps from URI, byte buffer and file.
-
Indoor positioning
Android developers with Android Pie can build indoor positioning support in their apps with native support for Wi-Fi Round-Trip-Time (RTT). If the hardware is present on the device, they can use RTT APIs to find relative distance from an absolute Wi-Fi Access Point.
-
Open Mobile API
Google brings GlobalPlatform Open Mobile API to Android Pie. Android app developers can now enable apps to use the OMAPI API to access secure elements (SE) to enable smart-card payments and other secure services.
-
Optimizations around Kotlin
Android Pie brings several compiler optimizations to Kotlin, especially those that target loops, to extract better performance.
A Modern Android
As part of Android 9 we are modernizing the foundations of Android and the apps that run on it, as part of our deep, sustained investments in security, performance, and stability.
Google I/O 2018: What’s new with Android Development Tools

“Make good things together” was the first thing flashing on the screens at Google I/O 2018 developer conference.
Google I/O 2018 developer conference being the biggest event of the year kicked things off with jam-packed news. In spite of tight competition, Google has set its sight on becoming the world’s biggest artificial intelligence company, and CEO Sundar Pichai proved that at the conference.
He outlined its idea about the software plans for the coming year and aspects of Artificial Intelligence included in it. During its I/O keynote, Google demonstrated the subsequent version of its Android operating system,
talked about the revamped Google’s news, and added features of personal assistant to it. Moreover, the company focused on making development easy and fast, helping developers to increase engagement and building the apps smaller in size.
Here’s a rundown of just about important things Google announced at the keynote:
Android Jetpack – Unified toolkit for Android developers
Android Jetpack is the next generation of Android components and Android support library that helps in managing things like background tasks, navigation, paging, and life-cycle management. Jetpack is divided into 4 components
- Foundation: Includes core system capabilities like app compat, Android KTX, Multidex, Test
- Architecture: Helps to search for the module that can further manage life-cycle, paging, navigation, data binding, work manager
- Behavior: Includes the module such as notification, permission, download manager
- UI: Contains UI-focused components like fragment and layout
Android developers can download Android Studio 3.2 or higher and start using Activity & Fragment + ViewModel template to include Jetpack in android app development
1. ML Kit to bring Machine learning to AI
ML Kit brings Google machine learning expertise to mobile developers in a powerful and easy-to-use package. It consists of API that will help Android developers to include image labeling, text recognition, face detection, barcode scanning, landmark detection, and many more.
The best thing is, it is available on both online and offline platforms and can be accessed in real-time. Developers can use API with little prior knowledge of machine learning and can be used on both iOS and Android platforms.
2. Introduced Android app bundle
Google introduced an Android app bundle that makes the app radically smaller. It enables users to install apps quickly and save space on their devices by downloading the code and resources required to run your app.
A developer can put everything needed for an app to run on multiple architectures and in multiple languages into the console and create bundles that contain only the files particular for user needs.
3. Koltin Performance improvements
Koltin is improving and this conference majorly focused on further enhancements. It has a collection of modules that contains extensions that optimizes the Android platform. Tooling continues to improve with Android Studio, Lint support, R8 optimizations, and Android runtime in Android P to build apps faster.
Using these extensions, developers can make minor improvements in the code. Koltin code snippet is available in the official documentation which is a great resource for developers who are new to Koltin.
4. Slices to increase engagement
Slices enable the user to interact with the apps that are already installed and provide users with a mini snippet of an app when searched in Google search and Google Assistant. Google has developed a new API that enables to the placement of snippets of the installed apps in Google search, Notification bar, etc.
This helps the users to get something done quickly and easily. For instance, if a user types “I want to book a ride” in a search box, they will see the mini version of the app over there without having to open the main app.
5. Android Instant apps to build apps with ease
Google launched a public SDK that is available to everyone for developing instant apps. Google has also built support for this feature into the new Android Studio and IDE enables the developers to modularize apps with ease.
For developing instant apps, they need to do is modularize the app properly on the basis of isolated features which can refrain them from creating a new app or maintaining a separate codebase. An official in-depth guide with code samples is available from Google that enables developers to build apps anytime
6. Android P is getting personal
Android P will also bring some new APIs which will let developers know how long the app is in use and how it’s used and can also advise them to put the phone down if it is a long time use. On Android P, device manufacturers will implement things like iris scanning through secure elements on the hardware easily. Moreover, UI elements, notifications, and assistants will look extravagant on Android P.
Other “AI” Announcements Made in Google I/O 2018
1. Google Assistant
Google came up with a new update in their Google Assistant service to create to-and-fro interaction with users. These include:-
- Six new voices, both male and female
- Continued Routines that enable users to design and activate with a preset phrase
- Continued Conversations that enables users to ask follow-up queries without tapping “Hey Google” for the second time
- A feature called “pretty please” aims to teach better manners to kids
This new service in Google Assistant just got better and more convenient for users. It aims to become completely realistic and simple for new and old Android users.
2. Google Photos
Google added new features to Google photos many of which are based on Artificial intelligence. The app will enable users to do things like colorize old black-white photos, fix the brightness of under-exposed photos,
and “pop color”, which colors the subject of the photo and sets the background to grayscale. Moreover, the app will also recognize when users are in the photos and will enable quick sharing with the tap of a button.
3. Google News
Google is putting emphasis on artificial intelligence for the new version of Google news. When app is opened, the user will see new headlines, local news, and more, and would offer a “full coverage”
section that will allow the user to see multiple stories from different sources. Users will be able to subscribe to content in an easier way without having to put in credit card information.
4. Gmail
Gmail will be able to write emails for users with only a few keystrokes. It will have a Smart Compose feature and would recommend phrases for the users when they start typing them, pulling from huge emailing history.
The feature will operate in the background and when the user types, grayed-out pops up will be recommended; the user needs to hit the tab button and suggestions will become a part of your mail.
Conclusion
Google I/O 2018, is all about Digital well-being! Understanding user preferences, Google focused on machine learning algorithms to do day-to-day tasks. The app development ecosystem will become flexible, adaptive, and quick;
however, mobile app development companies need to pace up with the evolving technologies for adapting to the changes being made on the technology front.






