Blog Tag: Node.js
Everything You Need to Know About Node.js for Backend Development

The digital world has grown in leaps and bounds in the past few years. Spurred by the pandemic, the physical world – in an unprecedented manner – made a shift to the digital world.
This, in turn, raised expectations in terms of operational efficiency among businesses. Today, businesses are adopting and adapting to technological advancements to keep up with the changing industrial landscape.
The challenge, however, lies in picking out the best tech stack. This is where the most popular and trusted modern application framework – Node.js – makes its entry.
Node.js development services are extremely popular as this framework is being used by a wide range of businesses such as Netflix, Twitter, etc. for their server-side application development.
StackOverflow’s 2022 Developer Survey shows that Node.js was chosen by 47 percent of its respondents and hence earned its position as the most popular web technology among web developers.
If you are wondering what Node js development services are and how they can add value to your business, read on to learn everything about Node.js!
What is Node.js?
In technical terms, Node.js is described as a single-threaded, open-source, cross-platform runtime environment that facilitates the development of server-side and networking applications that are fast and scalable.
In simpler terms, Node.js offers a balanced intersection of frontend and backend technologies. This means that it extends the capability of JavaScript to run on the server side of both web application architecture as well as serverless architecture.
If an analogy is to be drawn, Node.js is comparable to Java which also runs applications in its runtime. The ease of use and efficacy of Node.js is the reason for the boom in Node js development companies in the USA.
Node.js Frameworks / Approaches
Node.js is on its own an extremely powerful and versatile platform. However, several frameworks and approaches have also been developed to increase the efficiency of Node.js.
Here is a quick snapshot of these frameworks that contribute extensively to Node.js development services:
NestJS
NestJS is built on an abstraction of other Node.js frameworks such as Fastify and Express. This framework is extensible, versatile, and open-source and includes TypeScript, which is a subscript of the popular JavaScript. The abstraction makes this framework easier and faster for developers to learn and work on projects.
Modules, providers, and controllers form the foundation of the NestJS foundation. The first concept – Modules- is nothing but logical units of code put together. All applications need at least one root Module.
However, depending on the code organization, web developers may build more Modules on top of the code. The second component – providers – are abstractions of the code that can be injected at a certain stage as dependencies.
The third and last component – controllers – front end by taking in client requests, executing application logic, and responding.
Due to its ease of use and extensibility, NestJS is quite popular and offers a host of benefits. They are great for developing microservice architecture, lend a strict project structure, and enable a team of programmers to undertake a less bug-ridden development process.
ELECTRON
Electron combines the Node.js runtime with the Chromium rendering engine and facilitates the easy development of desktop applications on JavaScript. Furthermore, it also allows programmers to develop desktop applications in HTML5 and CSS, which are platform-agnostic web languages. Overall, it makes packaging and installation of these applications easier.
Electron is best suited for businesses that require desktop applications. Its framework allows speed up the development process and, therefore, it can be extremely helpful for a business that is looking for quick marketing of its new products.
DENO
The third framework – DENO – addresses the most critical aspect of the application – security, compatibility, and modules. DENO was introduced in 2018 by the creator of Node.js specifically to address the challenges that developers were facing.
The advantage that DENO offers is that the runtime executes in a sandbox safely isolated from the file systems. As a result, attackers are prevented from breaking out and securing access to the server the code is running on.
By allowing modules to be directly imported by a URL, DENO does away with the necessity for a centralized package management system. Also, DENO supports TypeScript which enhances browser compatibility – thus earning its popularity among web developers.
Why Use Node.js?
The popularity that Node.js and the surge in demand for Node.js development services are because of the ease it offers and its applicability in different types of use cases.
Here are a few reasons why you should use Node.js:
Applications are Lightweight and Fast
Node.js is particularly useful when it comes to building small, fast and scalable applications. Collaboration tools and instant messaging apps are the best examples. When coupled with fast synchronization abilities, Node.js can be useful for event-based applications too.
Flexible and Useful in Building Serverless and Microservice Architecture
Node.js is an extremely flexible framework that allows it to be used for the development of serverless and microservice architecture.
Both design styles are extremely popular because they help in saving resources and efficiently manage application lifecycles.
This is nudging more and more businesses across the globe to engage in Node.js development services.
Internet of Things
Node.js is efficient at handling multiple connections and hence works well with IoT. Node.js can successfully handle small messages that are relayed over multiple devices and hence it is very efficient when applied to IoT.
Processing Audio or Video
Another area where Node.js finds much application is processing audio and video. This is because Node.js can much more effectively handle asynchronous input and output. For instance, you can easily and quickly configure a streaming setup using Node.js.
Minimal Ramp Up Times
Because Node.js is built on common web languages, it is very easy to use and hence cuts down on ramp-up time and engineering resources, significantly. Cost efficiency is one of the major reasons for companies to engage in Node js development services.
Integration with C++ Code
As the Node.js runtime is built on a C++ server, it can seamlessly integrate with C++ libraries. As a result, Node.js quickly transmits data between the application code and C++.
How is Node.js Different from Other Backend Technologies?
Each framework is distinct and designed for a specific purpose. While the differences may not be blatantly apparent, they do exist.
Here is a quick comparison of Node.js with Java and Python.
Node.js Vs Java
Node.js and Java are often compared because both run their programs within their own runtime environment. However, there is a clear distinction between the two.
Java has a syntax similar to C++ and is an object-oriented programming language. This makes Java-heavy to use and costly to develop.
Node.js on the other hand is lightweight and based on non-compiled programming languages such as JavaScript.
Node.js is preferred for I/O applications for this reason. Furthermore, its efficiency in handling server-side HTTP requests is another reason that adds to its popularity.
Node.js Vs Python
Python is also widely popular among developers because of its simple syntax and ease of use. However, Python is more comparable to Java in terms of its object-oriented language.
While it is interpreted like JavaScript, its programs are seen to consume a sizeable volume of computing resources.
When Not to Use Node.js?
Node.js is not recommended for application development for fintech. The reason for this is the specifics of work with the floating decimal point that can lead to an accumulation of errors.
Similarly, it is not the best choice when it comes to working with heavily loaded threads that involve a CPU.
Trends in Node.js in 2023 and Beyond
Gauging by the popularity that Node.js enjoys currently, it would be safe to say that it will see much more adoption and integration as the world of business transitions into a more web-driven world.
However, some other Node.js frameworks will also see greater adoption in the coming years.
Frameworks such as Deno are expected to see more adoption due to their modularity and extensibility.
Similarly, Bun, which is a new runtime for JavaScript and TypeScript holds much potential as it offers higher performance and speed.
Amplify, which is a full-stack framework by AWS, and Remix – a newer web technology – is expected to trend in the coming years.
Need expert advice? Reach out to the experts at Tops Infosolutions!
Choose Our Custom Development Services for Your Future Project
If you are looking for hyper-efficient Node.js development services – Tops Infosolutions is the name, you are looking for.
We are pioneers in Node.js development and service clients across the globe. From developing business applications based on MEAN stack to delivering full-stack JavaScript frameworks, Tops offers a range of scalable solutions.
To know more, you can write to us at contact@topsinfosolutions.com or call us at +1 408 400 3737.
Six Powerful Web Applications You Can Build with Node.js

Did you know Node Package Manager or npm is the largest software registry on the web? This is coming from a web technology that wasn’t available on until 2009. Node has built a strong and ever-growing community & ecosystem around itself. Stack Overflow’s developer survey for 2018 shows that Node and two of its frontend counterparts, React and Angular, are the most used technologies by developers and made many companies actively looking to hire Node.js developers.
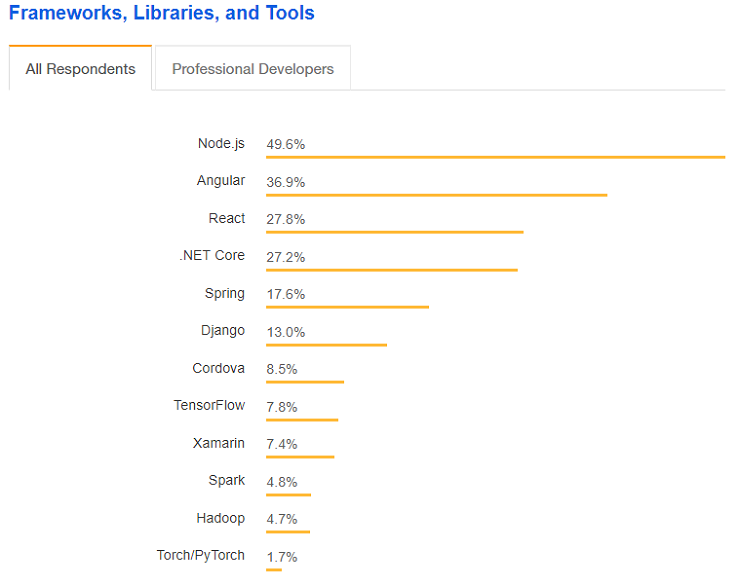
So what made Node.js so popular in such a small frame of time and why so many technology firms are talking about Node.js development services.
Well there are many benefits to Node over other backend technologies. The profound being its highly scalable architecture. I have already covered benefits and architecture of Node in the previous blog. In this blog, I will capture a few use-cases of web applications where Node finds the most relevance at.
Of course, real-time applications we interact with on a daily basis won’t be so many unless for Node’s scalable architecture.
1. Building Real-time Application
Uber’s extravagant ambition to make transportation as reliable as running water is reminiscent of the vast amount of IT resources that powers it and a reliable backend technology that powers those servers called Node. It’s not just Uber, thousands of enterprise and tech startups are building a substantial part of their backend infrastructure in Node to make way for real-time applications.

I mean they were still building real-time application before the time Node came. Those applications were inefficient and uneconomical because of higher resource utilization. When PayPal rebuilt one of their Java and Spring based applications using Node, this is what their blog cited.
“The node.js app was built almost twice as fast with fewer people, written in 33% fewer lines of code, constructed with 40% fewer files, processing double the requests per second, and measured 35% decrease in the average response time”
The technicalities how Node achieves this feat, you must refer my last blog on Node.js architecture. So next time you see an app updating data in real-time, think Node.js is behind it.
2. Server-Side Rendering (SSR) of JavaScript Application
Let me ask you a question. Can web apps written in JavaScript function without server-side rendering by a Node server? Yes, they can since web browsers can render JavaScript in addition to HTML and CSS on the client side. Then, why at all we need server-side rendering in JavaScript applications? The reason is search engine optimization.
Because a Single Page Application has a single URL for all the instances; it needs a router to generate fresh URL for major instances. However, responses of, Angular Router for example, is in pure and; often, async JavaScript, which web search crawlers such as Bingbot and Googlebot can’t comprehend.
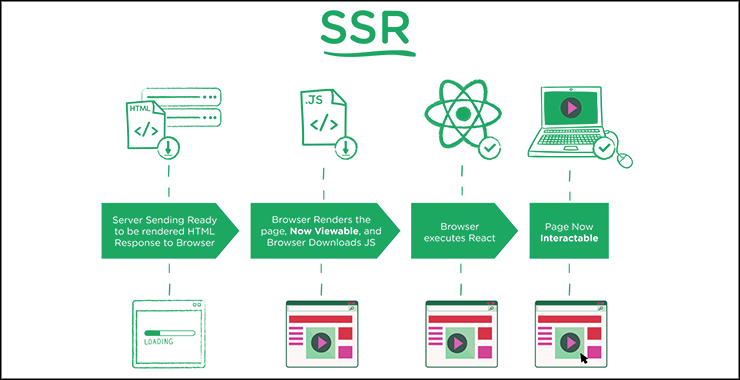
Therefore, web developers often have to rely on bringing Node.js developers to setup a Node server to enable server-side rendering on their SPAs. Since JavaScript is rendered server-side, web crawlers can crawl the instances of an SPA as they would pages on a dynamic website.
All major Node.js frameworks including Express and Koa support SSR.
3. Exposing MongoDB Data in MEAN Stack
Document databases such as MongoDB use JSON documents in order to store records; just as tables and rows store records in a relational database. Here is an example of a JSON document:
{ '_id' : 1, 'name' : { 'first' : 'John', 'last' : 'Backus' }, 'contribs' : [ 'Fortran', 'ALGOL', 'Backus-Naur Form', 'FP' ], 'awards' : [ { 'award' : 'W.W. McDowell Award', 'year' : 1967, 'by' : 'IEEE Computer Society' }, { 'award' : 'Draper Prize', 'year' : 1993, 'by' : 'National Academy of Engineering' } ] }
If you’re using Rails, you would convert from JSON to binary models, then expose them back as JSON over the HTTP when the data is consumed by React.js, Angular.js, etc., or even plain jQuery AJAX calls.
When using Node, though, you expose your JSON documents with a REST API for the frontend to read. A JSON database returns query results that can be easily parsed, with little or no transformation, directly by JavaScript—reducing the amount of logic you need to build into your application layer.
4. Handling Concurrent Streams to MongoDB
MongoDB access is a blocking operation, which could be a bottleneck to your Angular application when working on the MEAN stack since Node can virtually handle millions of requests at a time. This fallacy causes great strides of discontent with overall working of an application that gets thousands of concurrent requests.
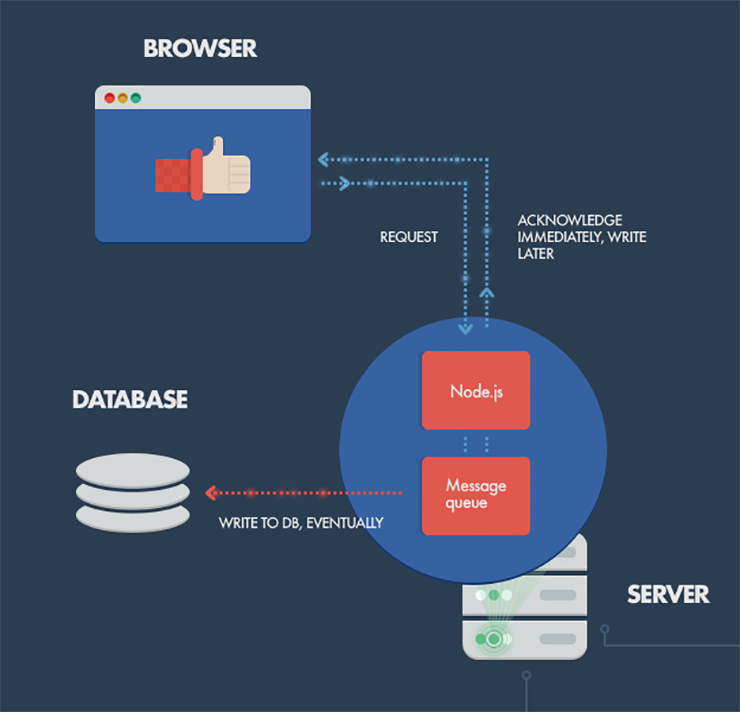
Node can turn out to be savior in those instances as it can accept the client’s request before the write operation on the MongoDB database. This approach is appropriate in applications where client doesn’t need instant confirmation on his actions leading to writes on the database. Node, in the meanwhile, can maintain system responsiveness under a large load.
5. Building Proxy Servers
Node.js is easily employed as a server-side proxy where it can handle a large amount of simultaneous connections in a non-blocking manner. It’s especially useful for proxying different services with different response times, or collecting data from multiple source points.
An example: consider a server-side application communicating with third-party resources, pulling in data from different sources, or storing assets like images and videos to third-party cloud services.
Although dedicated proxy servers do exist; using Node instead might be helpful if your proxying infrastructure is non-existent or if you need a solution for local development. By this, I mean that you could build a client-side app with a Node.js development server for assets and proxying/stubbing API requests; while in production you’d handle such interactions with a dedicated proxy service (nginx, HAProxy, etc.).
6. Real-time Dashboards
Node is prefect suit for building dashboard for displaying real-time data to users. For example, stock trader’s dashboard, application monitoring dashboard (Node-with-web-sockets), and system monitoring dashboard.
With the Node.js event loop, we can build powerful web dashboards to check service statuses in asynchronous manner and push data to clients using websockets.
Node matters more than any web technology ever around
Node.js is not only revolutionizing backend web development; it’s also bringing performance to the frontend application build in React, Angular and other frontend JavaScript frameworks and libraries. It brings noteworthy engineering to client-side. It plays an integral part in development of overall JavaScript ecosystem; the perfection of modern JS frameworks and, of course, technology stack building the future of web development—MEAN.
How to Use Node.js Architecture to Build Highly Scalable Apps?

Node.js is ideal for building highly scalable, data intensive, real-time back-end services that power our client applications. You might ask but there are other tools and frameworks out there for building back-end services such ASP.NET, Rails, Django, etc., why choose Node? Before answering the question, let’s understand Node.js architecture.
Node’s “Single Thread” Architecture
Node applications are highly scalable because of the non-blocking or asynchronous nature of Node. What do you mean by asynchronous? As a Node.js developer, let me give you an analogy.
You go to a restaurant. A waiter comes to your table, takes your order, and gives it to the kitchen. Then the waiter moves to serve another table while the chef is preparing your meal. The same waiter can serve many different tables and don’t have to wait for the chef to cook one meal before serving another table.
This is what we call non-blocking or asynchronous architecture and this is how Node applications work. The waiter is like a thread allocated to handle a request. So a single thread is used to handle multiple requests.
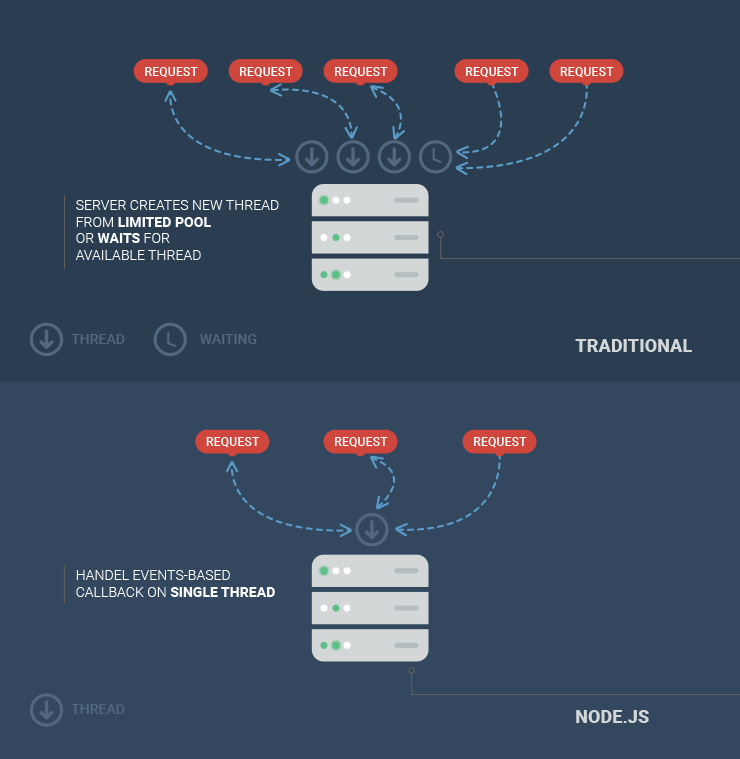
In contrast to non-blocking or asynchronous architecture, we have blocking or synchronous architecture. To understand the latter architecture, let’s go back to our restaurant analogy. You go to another restaurant, and in this restaurant, a waiter is allocated to you. The waiter takes your order and gives it to the kitchen. Now he is sitting in the kitchen waiting for the chef to prepare your meal, not doing anything.
One way to look at this analogy is this that the waiter is just waiting. He will not take an order from another table until your meal is ready. This is what we call blocking or synchronous architecture. Now, coming back to your question, that’s how applications built with frameworks like ASP.NET, Rails, and Django work out of the box.
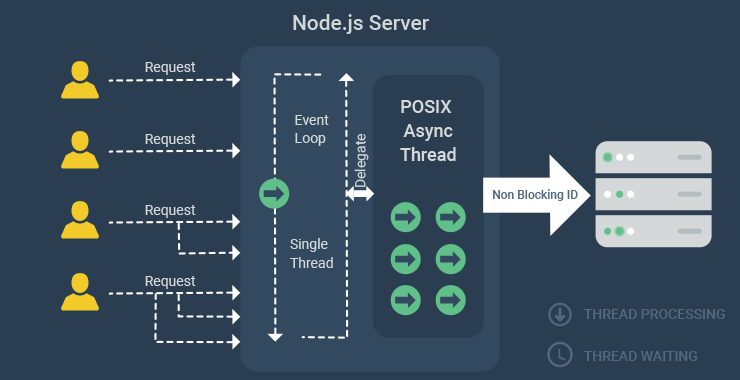
In this architecture, when a server receives a request from the client, the thread is allocated to handle that request. As a part of handling that requests, the thread might query a database, which may take a little while until the result is ready. When the database is executing the query, that thread is sitting there waiting. It can’t be used to serve another client’s request and the server has to allocate it another thread.
If we have a large number of concurrent clients with their requests, at some point we’re going to runout of threads to serve these clients. New clients have to wait until free threads are available. If we don’t want them to wait, we need to add more hardware. That’s why Node.js development companies are in great demand these days.
A real-life example
The real-time chat app to support your helpdesk is based on blocking or synchronous architecture and, consequently, for each new conversation, the app creates a new thread. Let’s say each thread occupies 2MB of RAM and the server has 8GB of RAM installed. The RAM will max out at 4000 concurrent conversations. If you have managed a chat support center, then you know 4000 conversations at a time aren’t surprising. Upgrading server, we all know is a costly affair.
In contrast, a Node.js based real-time chat app can, virtually, achieve scalability levels of over 1M concurrent conversation on a single thread in the same amount of RAM. Of course, even the largest of support centers don’t process this many requests at a time. This is the magnitude of scalability a Node.js application can deliver.
Node’s “Single Thread” Advantage
In blocking or synchronous architecture, we are not utilizing our resources efficiently. That’s why applications built with frameworks like ASP.NET aren’t exactly scalable as they max out at the hardware’s maximum ram.
On the other hand, Node.js Platform uses “Single Threaded Event Loop” architecture to handle multiple concurrent clients. Node.js Processing model is JavaScript Event based model with callback. This is how the model works.
Node web server accepts requests and puts them in event queue. The web server continuously polls for new requests from client in an infinite loop called Event Loop. Event loop is at the heart of Node.js applications and gives them the unparalleled scalability I am talking about.
The event loop operates under single thread in Node. The event loop runs endlessly across the event queue, seeking new client requests. If it finds a new request in the queue, it will flag it as either blocking or non-blocking. The event loop will process the non-blocking request and send the response to user.
Things get a little interesting when the request requires server to perform a blocking I/O operation like accessing the file system or raising a SQL query. In that case, event loop assigns that request a thread and goes about polling for fresh requests in the event queue. The thread, in the meanwhile, processes the thread, performs blocking operations, and sends it back to the event loop with a response. The event loop sends the response back to the client.
An ideal architecture to build scalable apps
Asynchronous architecture makes Node ideal for building applications that include a lot of disk or network access. Your application can serve more clients without the need to throw in more hardware. Thus, Node.js applications are highly scalable.
Secure Your Web App Against Modern Web Threats Using MEAN Stack

MEAN stack brings full stack development under purview of a single programming language, JavaScript. Alongside bringing the best of the frontend and backend technologies under a single basket, MEAN stack inherits security vulnerabilities each of these technologies are susceptible to. Some of the security threats augment when these technologies play together inside the framework. If those vulnerabilities are not subsided by the MEAN stack developers at the time of writing code, they will put the entire organization using those applications at jeopardy.
For example, MongoDB is a NoSQL database and an integral part of the MEAN stack. A common myth is NoSQL means no injections. In reality, MongoDB has a concept of query selector operators. These operators start with a dollar sign: $gt means greater than, $ne means not equal to, $not for negation, etc. If an attacker can inject these queries selector operators into the query, he can alter the logic of that query.
Here the presence of Express.js in MEAN stack makes the situation worse; it acts as a catalyst to NoSQL Injections. When Express sees nested URL encoded parameters in an input, it’s going to automatically parse them. This allows a person to inject a query operator into hid statement and alter the logic of this operation. And that’s only a part of the problem with MongoDB and there are three more technologies with their own share of risks and vulnerabilities.
Let’s take a look at the all the technologies inside MEAN stack and what are the potential security risks they can expose your application to.
1. MongoDB
As I said, MongoDB is immune to SQL injections but not every type of injections. In fact, MongoDB are more susceptible to something called Query Selector Injections or NoSQL Injections than MySQL is to SQL injections. The JSON documents with some neat, little tricks can be altered to achieve some malicious results. This as I mentioned above involve built-in logic operators to alter queries.
Another problem with MongoDB is this that it doesn’t force authentication that means that five year old hacker living next door can query the database with little to no difficulty. The icing on the cake is MongoDB’s optional HTTP and REST interface, which not only puts the database and the sensitive information inside it on the public domain but also the underlying file system.
To make sure, your database is not accessible to anybody make sure you disable HTTP and REST interface. You can configure /etc/mongodb.conf file’s bind_ip, auth,httpinterface, and rest options to contain access to the database and, thus, secure the MongoDB instance as demonstrated below.

Ransom-wares targeting the insecure default conf file on these servers exploited more than forty thousand instances of MongoDB by January 2017.
2. Node
Node.js facilitates the development of web applications with broad backend capabilities:server and networking capabilities. It makes way for real-time bidirectional communications back and forth from server and client. Node.js is a standalone package of Google’s V8 JavaScript engine and; thus, works outside of a web browser.
Developers love Node.js as it allows creating HTTP web servers while building the web applications. The very reason MEAN stack exists; Node.js isn’t without its share of security vulnerabilities. In fact, it inherits all security flaws JavaScript suffers from. In addition, the ability to execute at the server exposes it to a new set of attack vectors. Nevertheless, the CVE database compiles an up-to-date list of Node.JS vulnerabilities.
In a nutshell, full stack development may be the epitome of DevOps; nevertheless it necessitates stringent adherence to protected application development practices. The MEAN stack, and any stack for that matter—be it LAMP, .NET, or MEAN—needs apt controls to make sure that security is baked into an application since the initial phases of development. In the MEAN stack, complete vulnerability assessment and monitoring for web applications, databases, and servers is required.
3. Express
A minimal, flexible web application framework built around Node.js, Express hasmany features that simplify web and mobile application development. Express.js is to Node what Ruby-on-Rails or Sinatra is to the Ruby language.
Unluckily, the framework is susceptible to numerous injection and cross-site attacks and is vulnerable to all of Node.js’s core vulnerabilities.
For example, in MEAN stack, session state client-side stored in JSON Web Token (JWT) is encrypted. Thus, persistent session data server-side makes the application scalable when deployed in clustered servers. However, this handiness comes at a cost, explicitly the incapability to nullify a user’s session. Of course, you can expire the cookie afteryet the server will accept a replayed cookie even when you purged the cookie.

This issue can be moderated by keeping an inner expiration value within the session cookie.
Another problem with Express is this that the Csurf plugin is omitted from GET, HEAD, and OPTIONS methods. Csurf plugin protects web application from cross-site request forgery (CSRF). That is, an application with GET routes will not be protected from CSRF attacks.
That means the below code and the resulting app is vulnerable to CRSF because of the GET part.

To mitigate this, developers should do one of the following:
- Change the /secure/remove Invoice route to use the POST method
- Remove GET from the ignore Methods option
- Apply the Csurf middleware inline to each route requiring protection rather than globally with use()
4. Angular
Angular has inherent Strict Contextual Escaping service ($sce) by default. This service secure Angular from malicious HTML tags (e.g., <script>, etc.), attributes (e.g., onmouseover, onerror, etc.), and URI protocols (e.g., javascript) from data rendered as HTML with the ng-bind-html directive.
The problem is Strict Contextual Escaping service ($sce) can turned off by sceProvider.enabled() method globally while $sce.trustAs methods turn it off per-instance. In short, Angular is quite vulnerable to cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks when binding insecure data as HTML.

The easiest method around this vulnerabilities is to enable $sce service for untrusted bound to the ng-bind-html directive. Removing the $sceProvider.enabled(false) method from the excerpt above means the malicious onerror attribute will be sanitized appropriately.
Another security risk with Angular and thus MEAN stack applications is expression injection. An attacker can enter a curly bracket to Angular template to modify expressions. Aforementioned functions do not take in account expression injection using curly brackets.
To mitigate the risk, sanitize curly brackets from insecure input or by prevent the input from being written inside an Angular template by reducing the scope of the ng-app directive.
Conclusion
MEAN stack development is the epitome of DevOps that forbids insecure development practices. Besides, this approach entails sufficient controls to make sure that security is an integral part of every stage of development.
LAMP vs. MEAN Stack: Choosing the Right Fit for your Project

E-commerce platforms like Amazon, Walmart, eBay, Alibaba, etc. provide the best user experience and that’s the reason they are always on top of trends and can respond to millions of requests within seconds.
It is all because they have used the best business model which is supported by influential technology. Have you ever thought how huge such kind of system would be? What it would take to reach such great heights?
Let’s figure it out…
To develop such a web-driven application, it should be supported by technology like Apache Tomcat as the web server and PHP and J2EE as the development framework. For years, LAMP is serving as the go-to technology as it is involved in Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP, Perl, and Python.
Although LAMP is a good technology to deal with, it is a conventional approach to handle large database web applications. So, this technology is replaced with MEAN (MongoDB, ExpressJS, AngularJS, and NodeJS) to provide faster and more efficient web development due to JavaScript compatibility.
Since it works on the REST API, web apps can be developed by multiple front ends and the same back end; hence reduces the cost of developing the back end. Moreover, you can replace Angular.js with any framework that suits best the system.
Why MEAN is the Best For Your Enterprise Compared to LAMP?
-
MongoDB vs. MySQL:
MongoDB is considered a modern NoSQL database with a number of features and compatibilities. The strength of MongoDB lies in the relational databases compared to MySQL. When a relational database is used in MySQL, it feels like data is pushed into the table forcefully.
The system works perfectly when a single entry fits into every single format but fails badly when it doesn’t happen. On the other hand, MongoDB offers a document structure that is more flexible. So, if you wish to add new fields then simply add the field to the form, roll it up with the rest of the Data in the JSON document, and put it into the MongoDB collection.
This is great for the data dealing with dynamic data which is difficult to constrain in table form.
-
Makes your UX better with front-end
One of the major reasons to shift from LAMP to MEAN is to migrate from server-side page generation to client-side single-page applications. In MEAN, Express.js works on the REST structure and handles server-side routing and Angular.js handles client-side views.
The web-page presentation and control flow task in LAMP which was handled by PHP, Perl, or Python is taken care of by Expres.js and Angular in MEAN. Additionally, Angular.js also handles the data presentation of an application. Hence, this shift is from synchronous to asynchronous processes and page-centric views to component-oriented views of an application.
Moreover, being back with an excellent JavaScript front-end framework, the web app runs efficiently, making the UX smoother. With all such parameters in the mean stack, it enables the web application to run on desktops, laptops, mobile phones, tablets, etc.
-
The Code
MEAN makes use of Express.js and Angular.js to drive the web page presentation and control flow. Express.js serves as a controller layer, controlling application flow and organizing data for Angular.js, which handles data presentation. The importance of this is, it has simplified back-end architecture.
If you write the code for Node and decide to place it in Angular, you can do it with ease. This flexibility makes MEAN-based apps significantly easier. You can have the added benefit of having an entirely single language and don’t have to look for additional developers like a PHP expert, JavaScript experts, or front-end or back-end specialists – just a front-end javascript developer to trace all the way down the stack without having to learn another programming language.
-
Node.js simplifies the server layer
Navigating various layers of the LAMP stack is like dancing on many hats; going through the various config files with different syntaxes. This sounds a bit clumsy. But, when it comes to MEAN, it simplifies this with the help of Node.js.
Sprinkle in some JavaScript whether you want to change how your app routes requests or want to change the logic used to answer queries you want to rewrite URLs or construct an odd mapping and let Node.js do the rest of the work.
The MEAN stack in combination with Node.js keeps everything in one place and one language. You don’t have to read the pages of PHP, generate different config files, etc as in LAMP. Having everything in one place reduces the chances of errors and confusion between multiple layers.
To be precise…..
LAMP stack has surely become a conventional approach but it holds good efficiency in the market over the years as many CMS still rely on LAMP. However, MEAN Stack becoming a new player provides new and innovative ways to cut the grounds.
MEAN web development has its own list of benefits to offer for flexible web development, especially for an organization that is looking to move its focus from LAMP to an advanced Mean stack technology.
Looking to develop your next big project in MEAN? We are just a call away!! Let’s connect.
Building Modern and Scalable Enterprise Apps with MEAN Stack

Why you Should Choose the MEAN Stack For Your Modern Business Apps
Today, web programming being one of the challenging tasks, especially in case of enterprise applications, business owners look for the technology that provides high performance and scalability.
Many enterprise leaders struggle to stand tall amongst competitors – so to deal with such requirements; web development companies have to deal with the host of technologies dealing with security, networking, databases and development of server-side and client-side components.
Although there do exists much powerful communities that provide solutions for the enterprise applications but the one that enables the modern web development is the full stack solution – MEAN Stack.
MEAN – the full-form for MongoDB, Express.js, AngularJS and Node.js which was possibly the much needed and awaited revolution for the technical sphere. This stack is crafted by diverse teams and considerable community of developers is also involved that pushes forward the development and documentation of each component.
And now that MEAN Stack is so much into the world of technology and business, every growing enterprise is striving to become MEAN friendly; leaving behind plenty of solutions who are still showcasing their loyalties towards older versions! The core thing in this stack is the centralization of JavaScript as the primary programming language.
-
MEAN makes switching between client and server easier
MEAN is simple & fast and developing the apps in this technology enables the developers to write the code only in one language i.e. JavaScript for client as well as server side. Entire project can be managed by MEAN Stack formula and Node.js developer can deploy the applications on the server directly without the need of deploying it to a stand-alone server.
Additionally, it is OS independent – be it Windows, Linux or MAC. This is the best for startups and enterprises as they just have to accommodate development framework and need not think on technology.
No need to waste time in scanning libraries as all JavaScript libraries can be combined with MEAN stack. The saved time can be utilized for other productive activities which are especially crucial in the case of Startups.
-
Facilitates speedy data storage and retrieval
MongoDB in MEAN Stack uses JSON like documents throughout the database which makes it a documented database. The document structure offered by MongoDB is extremely flexible. No hardcore restriction to forcefully enter data into tables to make it usable.
For instance: addition and deletion of data can be easily done without making any complex accommodations. MongoDB doesn’t require any predefined database schemas and rules to establish field relations like MySQL.
Hence, when no large schemas are present, the system becomes efficient and fast to use and ultimately benefits the end user increasing their confidence in the start-up offering their services.
-
Uniform code from start till end
With the sufficient knowledge of JavaScript developers, you can manage your entire project with ease. JSON like queries are already available in MongoDB database, hence JSON queries can be used with Express.js and Node.js server and can have similar format for all data transfer.
However, some angular queries can be used on client side using Angular.js. Furthermore, usage of express.js and angular.js on the top of node.js results into technology stack that gives the benefit of single language means the full stack developer can manage the stack easily without learning another programming language like Python or PHP.
The experts in JavaScript can go through the entire MEAN stack themselves and can control both front-end and back-end activities. This is quintessential because developers couldn’t code, if they don’t have core knowledge of all respective technology. Other than that, page load time can be substantially reduced with node.js framework.
-
MEAN stack supports MVC architecture
When it comes to MVC, there are four aspects that help the developers for easy execution; namely – database, server, client and client UI.
In MVC, the model responds to the request for any information or data manipulation according to the controller’s instruction. The controller on the other hand responds to the system that user needs and thus gives instructions to model.
To run MVC framework complex procedures, there are numerous stack frameworks on innumerable different programming languages. With one programming language and flexible database, MEAN stack is considered as influential alternative which can compile with MVC architecture very easily.
This enhances the productivity of developers and enables the application to load faster and also assures quicker project completions.
-
Regular component updates
MEAN stack components are open source, free to use and their respective communities and support channels do come up with frequent releases and updates.
More ideas and insights from the developer community and tutorials on how to overcome hurdles to emerging challenges help keep the products and services relevant to today’s economic of scale.
The overall framework is flexible and easy to understand by making it popular with enterprises and developers.
In a nutshell, many business owners make the use of MEAN stack to revamp their existing websites. It is also ideal for other web content like blogs, media websites, data-intensive and real-time messaging applications.
If you wish to develop you next big project in MEAN, our skilled consultants will help you craft the perfect business plan.
TOPS Infosolutions is a top Enterprise Software development company, having hands-on knowledge to quickly transform your idea into world class application. Powerful IT solution – MEAN and reliable technology partner will give that ‘extra edge’ to your business.



